ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION ON THE COURSE OF ACUTE INSULIN DEFICIENCY IN RATS
Kokaya Nikolay Grigorievich
THE INFLUENCE OF LOW-INTENSITY ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION ON THE COURSE OF ACUTE INSULIN DEFICIENCY IN RATS
(experimental study) 14.03.03 – pathological physiology
ABSTRACT
the dissertation on competition of a scientific degree
candidate of medical Sciences
Nizhny Novgorod – 2012
Work performed in State budgetary educational institution of higher professional education “Nizhny Novgorod state medical Academy” of the Ministry of health and social development of the Russian Federation
Scientific adviser: doctor of biological Sciences, Professor
Irina Vasilievna Mukhina
Official opponents: doctor of medical Sciences, Professor
Potemin Tatiana Evgenievna
(GBOU VPO “Nigga” health Ministry of Russia,
, Nizhny Novgorod)
doctor of medical Sciences, Professor
Peretyagin Sergei Petrovich
(FGU “NIETO”, Ministry of Russia,
, Nizhny Novgorod)
Leading organization: FGUO VPO “Military medical Academy named. S. M. Kirov” of the Ministry of defense of the Russian Federation, St. Petersburg)
The dissertation will be held”_____” ____________ 2012 year_____ hours at the meeting of the dissertation Council D 208.061.03 at Nizhny Novgorod state medical Academy of the Ministry of health and social development of the Russian Federation address: 603005, , Nizhny Novgorod, plasma Minin, D. 10/1.
With the thesis can be found in the library of the state budgetary educational institution of higher professional education “Nizhny Novgorod state medical Academy Ministry of health of Russia (603104, , Nizhny Novgorod, street Medical, doctor 3A).
Abstract distributed” _____ ” _____________ 2012 ,
Scientific Secretary
dissertation Council
doctor of medical Sciences, Professor Durnovo E. A.
General characteristic work
The relevance of the study. In recent years significantly increased attention to the problem of biological action of electromagnetic fields and radiation, comparable in intensity with the natural electromagnetic background. This interest is due primarily to the fact that a small amount of exposure causes biological effects, comparable, or even greater than the effects observed when the action is substantially higher doses [A. C. Karnaukhov, 2003; B. N. The Bing, 2005; D. A. Cherenkov, 2006]. The problem of studying the mechanisms superweak impacts on biological systems closely linked to the issue of the transfer of biological information, recording and storage in the cells and in the intercellular space and between organisms [E. B. Burlakova, 1990; R. Pomeranz, 1998]. Despite years of research, the mechanisms superweak impacts on biological systems remain poorly understood [Century. N.The Bing, 2005]. At the same time, on the basis of experimental data, some authors [E. L. Maltsev, E. P. Palmin, 1998] tend to assume that the electromagnetic interaction inside and outside biological systems have an important regulatory role in the control of physiological functions along with neurohormonal, humoral and biophysical factors.
A large number of works devoted to the use of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation in the treatment of diseases that are resistant to pharmacological agents and immune to most known methods of treatment [I. A. Myskina, 2004; E. C. Surkov, 2005; S. A. Dogadin, 2007]. One such disease that is difficult therapy, is diabetes. Increasing prevalence and incidence of diabetes has enabled the experts who recognize the presence of the diabetes epidemic of non-communicable nature [M. I. Balabolkin, E. M. Klebanov, 2007]. The complex pathogenesis of diabetes, a large number of severe complications, difficulty of treatment has made the problem of therapy of diabetes mellitus even more relevant. Currently, the main elements of the treatment of diabetes remains diet, insulin therapy, and the use of oral antidiabetic drugs. Physical methods of influence used primarily for the prevention and treatment of complications associated with diabetes [A. Y. Kekuewa, K. C. Agadzhanova, Acting Elizarova, 2010]. To date, there have been isolated indicate that low-intensity laser radiation could be used as a primary pathogenetic due to the method of treatment of diabetes [O. A. Lukin, 2009].
In experimental medicine model of alloxan diabetes is widespread, as alloxan selectively impairs β-cells of pancreatic islets, and the use of toxic doses of alloxan quickly causes rats to the development of acute insulin deficiency, coupled with toxic cell damage vital organs [R. Dawson, D. Elliot,1991]. This experimental model is very convenient for the study of pathogenetic mechanisms associated with carbohydrate metabolism, and allows you to quickly evaluate different methods of correction [N. N. Chernyshenko, 2004].
The purpose of the study. To explore the pathophysiological mechanistically low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, in conditions of experimental models of acute insulin deficiency in rats.
Objectives of the study.
1. To develop the method of action of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures (pEMP), in rats with acute insulin deficiency caused by the introduction of toxic doses of alloxan.
2. To study the influence of the corrective effects of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, during acute insulin deficiency in rats caused by the introduction of toxic doses of alloxan.
3. To investigate the influence of the corrective effects of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, on biochemical parameters of blood serum, morpho-functional state of the pancreas and liver in rats with acute insulin deficiency.
4. To study the effect of preventive effects of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, during acute insulin deficiency in rats caused by the introduction of toxic doses of alloxan.
5. To investigate the influence of the preventive effects of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, on biochemical parameters of blood serum, morpho-functional state of the pancreas and liver in rats with acute insulin deficiency.
Scientific novelty. As a result of research first developed the method of action of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, on rats with acute insulin deficiency.
First established that the proposed method contributes to the reduction of mortality and normalization of glucose level in blood in rats with experimental diabetes mellitus when correcting exposure and increase the resistance of animals to damaging agent for preventive application.
First it is shown that the corrective effect of this radiation contributes to the activation of regenerative processes in tissues of the pancreas along with the existing destructive processes, and the preventive effect of cytoprotective action and contributes to the development of hypertrophic and hyperplastic processes in the tissue of the pancreas.
For the first time revealed a reduction in the activity of pancreatic amylase and liver enzymes in rats with experimental diabetes mellitus in the result of exposure to low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures.
For the first time investigated the pathogenetic mechanisms of compensatory-adaptive and protective action of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, on the model of acute insulin deficiency in rats.
Theoretical and practical significance of the work.
The obtained experimental data extend the current views on the biological role of low-intensity electromagnetic fields, converted biostructures, and their importance in the regulation of the life of the organism.
The totality of the data and theoretical positions allows to evaluate the influence of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, on the course of experimental diabetes and pathophysiologically to explain the mechanisms of action of this type of radiation on biological objects.
The main provisions for the thesis defense:
1. The corrective effect of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, contributes to the activation of compensatory-adaptive mechanisms aimed at preserving the life of the organism, and activation of regenerative processes in the damaged organ in rats with acute insulin deficiency.
2. Preventive effect of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, exerts a cytoprotective effect, providing the resistance of animals to the action of damaging agent.
Implementation of research results.
The results of the study are embedded in research Central research Institute PFM GBOU VPO Nigga the health Ministry of Russia for further study of pathophysiological mechanisms superweak effects on biological systems and mechanisms associated with carbohydrate metabolism.
Approbation of the thesis. The materials of thesis presented to the school for young researchers “basic science and clinical progress of medicine” (Moscow, 2010), the final scientific conference “Tatyana’s day” (Moscow, 2010), the 4th international scientific conference of young scientists (Kursk, 2010), the 2nd international conference “Fundamental and applied aspects of medical Primatology” (Sochi, 2011),the conference “Psychotronic” (Kentucky, USA, 2010).
The dissertation is approved by the inter-departmental meeting of the chairs of normal anatomy, pathological physiology, normal physiology and the bmrc research Institute PFM GBOU VPO Nigga the health Ministry of Russia on January 20, 2012 (minutes No. 5) (N. Novgorod, 2012).
Personal contribution of the author was that he participated in the formulation and conduct physiological experiments were statistically processed data, and participated in the writing of scientific articles.
Publication. The thesis is published 10 scientific papers, 5 of them in journals recommended by the VAK.
Volume and structure of the thesis. Thesis presented at 145 pages of typewritten text, and consists of an introduction, literature review, three chapters of his own observations, discussion of results, conclusions and practical recommendations. The work is illustrated with 5 tables and 27 figures. Bibliography 230 includes sources of literature, of which 107 domestic and 123 foreign authors.
THE CONTENT OF THE WORK
Materials and methods study
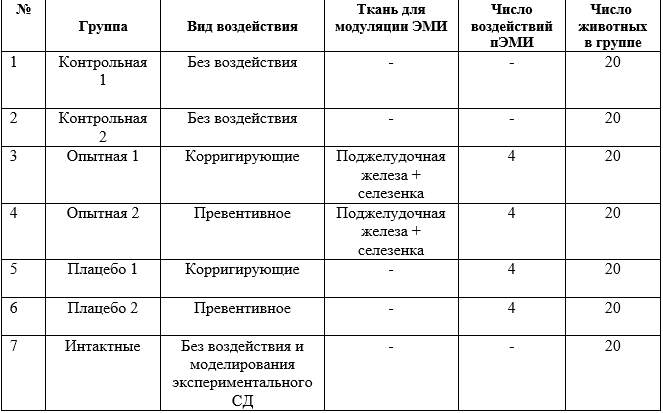
To achieve the job goals and objectives of the experiments were performed at 140 white laboratory rats male Wistar at the age of 5-6 months, weighing 180-220 g the Total number of objects of study and the distribution of the experimental groups is presented in table.1).
Experimental diabetes was caused by intraperitoneal administration of a solution of alloxan prepared extempore at a dose of 200 mg/kg, after a 24 hour fast on the background of normal levels of glucose in the blood.
Experimental animals were placed under observation in standard vivarium conditions. Every day for 1.5 months assessed the overall condition of the animals, the amount of fluid consumption, recorded the day mortality observed in all groups, registered level of blood glucose by glucometer AscensiaEntrust Bayer.
Table 1
The total number of objects of study and their distribution in groups
In the control and placebo groups, the blood from the sublingual vein for biochemical studies and the removal of the tissues of the pancreas and liver for pathological studies were carried out on 3 and 4-th day since the introduction of alloxan, which corresponded to the day of maximum mortality in these groups. In intact rats and in the 1st and 2nd experimental groups, blood sampling for biochemical analysis was performed on the 3rd day, the 8th day of the experiment and after 1.5 months since the introduction of alloxan. The removal of the tissues of the pancreas for pathological studies in experimental groups was performed on the 8th day and 1.5 months since the introduction of alloxan. Removal of liver tissue for pathological studies were performed in 1.5 months since the introduction of alloxy.
The content of glucose, total protein, albumin, alkaline phosphatase, AST, Alt, pancreatic amylase, creatinine and urea in blood serum of experimental animals was determined using a biochemical analyzer AB-02 Ural optical and mechanical plant at a wavelength of 500/600 nm (measurement mode end point) and a set of special reagents after centrifugation for 10 minutes.
For histological studies, tissues were fixed in 10% neutral formalin, obezvozhivani in ascending alcohols concentrations and embedded in paraffin. Paraffin sections with a thickness of 5-7 μm was obtained on the microtome LeicaSM 2000R, were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and analyzed using a microscope LeicaDMLS. The video received by the video system with CCD camera.
The obtained data were processed on a personal computer using the software package MicrosoftExcel and STATISTICA® for Windows, Release 6.0 (2006). To determine the reliability of data were used: quantitative normally distributed data – student test for nonparametric data Fisher’s exact test, nonparametric methods Mann-Whitney. For criterion validity was adopted value of p<0.05.
Effect of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures
As a source of electromagnetic radiation was used helium-neon laser power of 2 mW and a wavelength of 632.8 nm, which has two single-frequency, combined orthogonal linearly polarized fashion emission [gg Tertyshny, 1999]. The generation of electromagnetic radiation was performed according to the scheme of the Fabry-Perot interferometer, in which the working laser beam repeatedly passes through thin layers: top glass layer of cells svezhepriobretenny tissues of the pancreas or spleen healthy newborn rat Wistar (P2-4), a glass slide. Before the experiment seized organs (pancreas, spleen) in the amount of 3 mm3 was applied on a glass slide, covered with cover glass and placed on the optical axis of the laser beam. Align the glass with the drugs was performed in such a way as to ensure partial inverse reflection of the beam, modulated by drugs, in the resonator of the laser. Such multi-pass mode allows the drug to act as an optical correlator [Mazur, Grachev, 1985] and to affect the distribution of the secondary modes of laser radiation. Optical signals were recorded and submitted in an electronic circuit, which controls the mode laser with frequency stabilization of coherent radiation. In this mode of operation, switching power supply of the laser, which plays the role of a transmitter of electromagnetic radiation, generates the converted probe drugs electromagnetic radiation. The distance from the probe drug to the active element of the laser 11cm.
Figure 1 shows the signals recorded electromagnetic radiation of He-Ne laser in a state of resonance.
A 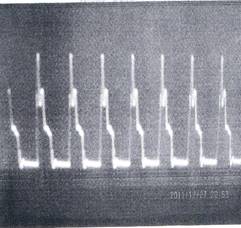
 B
B
Fig.1. The signal from the power supply of the laser in resonance mode without a biological object (a) and spectrum of the frequency-amplitude and phase components of the electromagnetic radiation of the scanned tissue of the pancreas (b).
To eliminate adverse influence of external factors for each experimental group formed in parallel the control and placebo groups. In the control groups (table.1) the effects of electromagnetic radiation have not been conducted. Animals of the 1st experimental group (table.1) were subjected to the corrective influence of electromagnetic radiation that is converted by the tissues of the pancreas and spleen of newborn rats (P2-4) (pEMP) with 3 days since the introduction of alloxan. Animals of the 2nd experimental group (table.1) carried out preventive effects of PAME, the day before modeling alloxan diabetes. Animals 1 placebo group (PL.1) was subjected to electromagnetic radiation that is not converted biostructures, starting with 3 days since the introduction of alloxan. Animals 2nd placebo group (PL.1) was subjected to electromagnetic radiation, also not converted biostructures and alloxan diabetes was modeled after the day after the last exposure. Animal experimental and placebo groups were placed at a distance of 70 cm from the source of electromagnetic radiation. The impact of PAME on the 1st and 2nd experimental group was carried out daily for 30 minutes for 4 days according to the scheme: 10 minute exposure pEMP obtained by passing the laser beam through the drug with the tissue of the pancreas; 10 minute exposure pEMP obtained by passing the laser beam through the drug with the tissue of the spleen; 10 minute exposure pEMP obtained by passing the laser beam through the drug with the tissue of the pancreas. The impact is not converted biostructures electromagnetic radiation on animals 1-St and 2-nd placebo groups was carried out within 4 days of 30 minutes daily. When the laser beam passed through the objective and the cover glass, not containing biostructure.
In the group of intact animals with experimental diabetes mellitus was not modelled and the impact of electromagnetic radiation is not performed.
Research results and discussion
Peculiarities of the course of experimental diabetes induced by toxic doses of alloxan
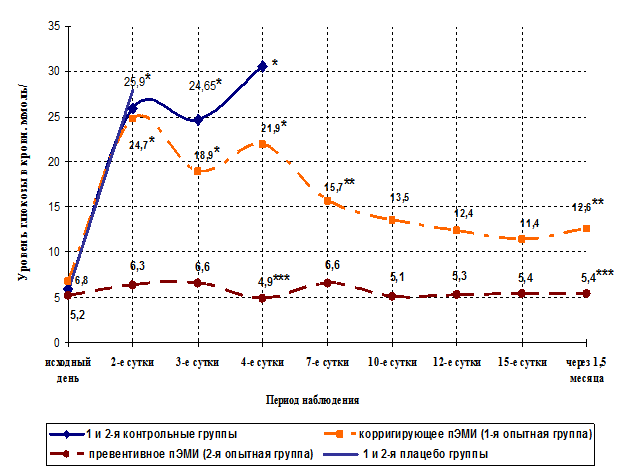
In the present study were the differences in the course of experimental diabetes in animals in the control and experimental groups. It has not been established differences during alloxan diabetes in animals of the 1st and 2nd control groups (p=0,8) and animals 1-St and 2-nd placebo groups (p=0,9). As it has not been established differences during alloxan diabetes between the control and placebo groups (p=0,6), however, there were significant differences in the course of experimental diabetes in animals 1-St and 2-nd experimental groups (Fig. 2) (p=0.03). After the introduction of alloxan at a dose of 200 mg/ kg in rats for 2-3 days developed acute insulin deficiency, accompanied by toxic damage to several vital organs and systems. Since 2 days since the introduction of alloxan, in animals from the control and placebo groups there was a marked hyperglycemia, and the average level of blood glucose was 25,93±8.16 mmol/l, which was significantly different (p=0.004) from the original values (Fig.2).
Fig. 2. Dynamics of glucose in the blood of rats in experimental groups after modeling of acute insulin deficiency
* the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the control, placebo and 1 experimental groups on 2nd, 3rd and 4th day after the simulation of experimental diabetes significantly differ (p = 0.004) of the initial value (Fisher’s test);
** – the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the 1st experimental group on the 7th day and 1.5 months after simulation of experimental diabetes significantly differ (p=0.03) from glucose level on the 2nd and 4th day of the experiment (Fisher test);
* * * the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the 2nd experimental group on the 4th, 7th day and 1.5 months after modeling experimental diabetes significantly differ (p=0.007) from the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the control, placebo and 1 experimental groups (Fisher’s test).
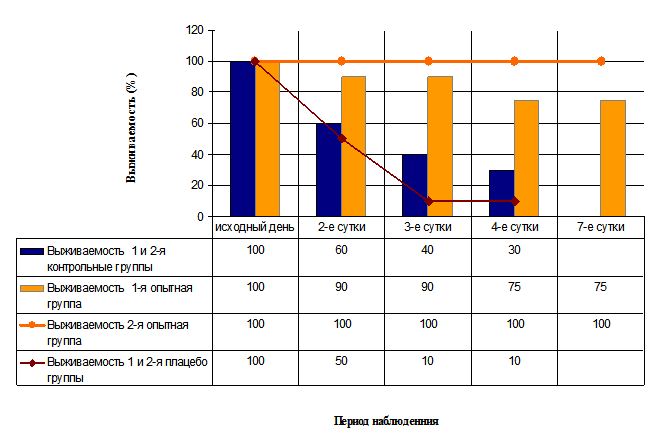
On the background of a sharp increase of glucose level in the blood and the development of hyperosmolar state in the blood serum of the rats of the control and placebo groups on the 3rd day since the introduction of alloxan there was a reliable increase in total protein content (104,0±4.9 g/l) and albumin (54,2±3.7 g/l) compared to baseline values (63,0±2.4 g/l) (p=0.04), and the indices in intact rats (63,5±2.8 g/l) (p=0.03), significant increase of the enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase (126,5±8,3 IU/l) (p=0.05), AST (225,8±10,4 IU/l) (p=0.02) and creatinine (168,0±6.8 µmol/l) (p=0.05), lower level urea and 0.7±0.2 mmol/l of level Values of the enzymatic activity of pancreatic amylase in the serum of rats in these groups has not increased significantly, which is a bad prognostic sign for life in acute pancreatitis. It should be noted that in these groups were absent spontaneous lowering the level of glucose in the blood and normalization of biochemical parameters of blood serum during the observation period (Fig.2). The survival of animals in the control groups was 30% and in the placebo 10% (Fig.3).

Fig. 3. Survival of animals (%) in experimental groups after modeling of acute insulin deficiency.
Morphological changes in the pancreatic tissue of rats in the control and placebo groups were similar and had a number of specific features. In contrast to intact rats histological examination of the pancreas in animals of these groups showed marked degenerative changes in the islets of Langerhans. The number and size of islets reduced form them wrong. The number of β-cells in the islets drastically reduced, most of them showed vacuolization of the cytoplasm, reducing the size of nuclei, condensed chromatin, in some cells – karyopyknosis. Revealed the presence of lymphocytic infiltrate around and inside parts of the Islands.
In preparations of rat liver in these groups discovered the preservation of the beam structure of the cells, the boundaries of hepatocytes expressed weakly. Core medium or large with the nucleolus. The total number of cells did not undergo significant changes compared to the intact, however, were found degenerating hepatocytes, and therefore, the amount of normal hepatocytes was less. The degenerating hepatocytes met hyperchromic nuclei of irregular shape (karyopyknosis), some cells the nucleus was absent. In most cells the cytoplasm loose with small vacuoles.
The effect of the corrective effects of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures
On the background developed acute insulin deficiency on animals of the 1st experimental group had a favorable impact of low-intensity ELECTROMAGNETIC radiation of He-Ne laser, converted tissues of the pancreas and spleen of newborn rat (P 2-4). The average level of glucose in the blood of the animals of the 1st experimental group on the 4th day since the introduction of alloxan amounted 21,93±to 9.91 mmol/l, which was significantly (p=0.02, Fisher’s test) differed from the original values (5,97±1,38). After exposure to 7-th day since the introduction of alloxane the average level of glucose in the blood of rats decreased to of 15.75±to 8.41 mmol/l (p=0.03, Fisher’s test) (Fig.2,4). In most cases (65%) after exposure to pemi the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the 1st experimental group was normalized, and 7 animals (35%) during the entire observation period (1.5 months) there was a strong hyperglycemia. Despite the persistent increase in the level of blood glucose in these animals, persisting over a long period, their death has not occurred, and the General condition was described as satisfactory.
On the 3rd day of the experiment rats in the 1st experimental group indicators total protein, albumin, creatinine and urea in serum remained within the normal range that was significantly different from the same parameters in the control and placebo groups (p<0.05). On the 3rd and 8th day of the experiment in the serum of animals of the 1st experimental group was observed a significant increase, compared with the original values, indicators of alkaline phosphatase (345,3±12,5 IU/l; p=0.01), AST (178,5±13,4 IU/l; p=0.03) and a significant increase in pancreatic amylase (4986,0±145,5 IU/l; p=0.002). 1.5 months after the introduction of alloxan in surviving animals showed normalization of biochemical parameters in blood serum. The survival of animals in the 1st experimental group on the 4th day since the introduction of alloxan was 90%, and by the 7th day decreased to 75% and remained at this level for 1.5 months, which is significantly different from survival in the control (30%) and placebo (10%) groups (Fig.3).
The histological pattern of the preparations of the pancreas in the 1st experimental group on the 8th day since the introduction of alloxan was characterized by signs of functional voltage operation of the cells of the islets of Langerhans. Was observed mainly small and medium-sized Islands. The share of the insular apparatus was reduced was determined vacuolization of the β-cells, reducing their number. Destructive changes were expressed in varying degrees. Characteristic histologic preparations of this group was the safety of the nuclei of islet cells zone of the gland. This was not observed in the preparations of the pancreas of control and placebo groups. After 1.5 months since the introduction of alloxane the histological pattern of the pancreas in the 1st experimental group was characterized by the presence of a large number of small islets correct form, normal histological structure near the blood sinuses and ducts. Along with this there were degenerative changes in different degrees of severity, the areas of inflammatory infiltrates in the stroma of cancer and multiple sclerosis. Such structural changes in the tissue of the pancreas speak not only of the transferred cytotoxic effects of alloxan on cells of the islet area, leading to degenerative changes, but also about the activation of regenerative processes.
In contrast to the control and placebo groups histological examination of preparations of rat liver 1st experimental group in the remote period (1.5 months) were identified and marked degenerative changes in the structure of the body. Broken beam arrangement of hepatocytes. In the parenchyma met lymphocytic infiltration. Most Central veins greatly expanded and often full. In portal tracts strong histolitica infiltration. Copperhouse cells moderately activated, the majority has an elongated shape. The increase in the number of Kupffer cells in rat liver is an indicator of a busy phagocytosis, which may be associated with more active liver for disposal of the decay products of different cellular structures. Hepatocytes little gipertrofirovannyy. It should be noted that most of the nuclei in the cells of the proper shape, well painted, with nucleoli. Also met hepatocytes with “holey” nuclei, cells without nuclei, or with pyknosis kernel. Binucleate cells was very small.
The effect of the preventive effects of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures
In the 2nd experimental group, animals which had a preventive impact of pEMP observed a more pronounced effect than in the 1st experimental group (Fig. 2, 3, 4). In this group has not been a single case of fatal outcome was observed 100% survival of animals during the whole observation period (Fig.3). 90% of the animals of the 3rd group after the introduction of alloxane the level of glucose in the blood remained within physiological norms during the entire observation period (1.5 months), which significantly differed (p=0.03) from the values of the indicator of the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the 1st experimental group (Fig. 2, 4).
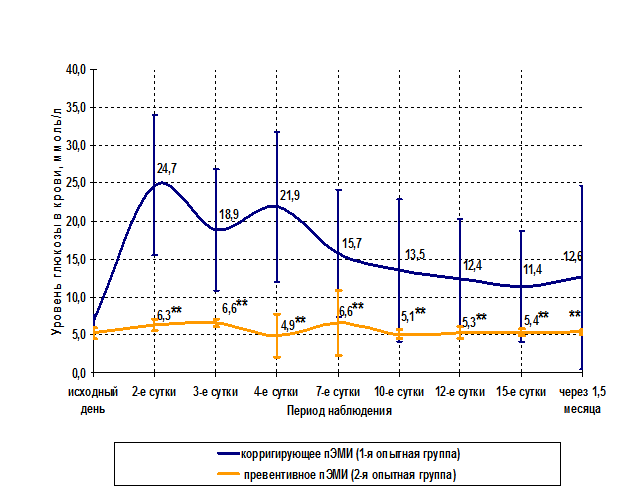
Fig. 4. Dynamics of glucose in the blood of animals 1-St and 2-nd experimental groups during the observation period, mmol/L.
** – the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the 2nd experimental group significantly differ (p=0.03) from the level of glucose in the blood of rats of the 1st experimental group (Fisher’s test);
During the observation of two rats of the 2nd experimental group to the 6-th day of the experiment was marked by the rise of glucose level in the blood more than 20 mmol/l, followed by spontaneous decrease to normal values. Changes of biochemical parameters in the serum of rats of the 2nd experimental group, in contrast to rats in the control, placebo and 1 experimental groups were less pronounced. However, on the 3rd and 8th day of the experiment it was observed a significant increase, compared with the original values, the enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase (123,7 ħ 9.8; p=0.04), AST (156,8±23,4; p=0.05) and pancreatic amylase (1238,8±235,3; p=0.008), which is associated with the cytotoxic activity of alloxan. 1.5 months since the introduction of alloxan rats in the 2nd experimental group were observed normalization of biochemical parameters in the serum. During the whole period of monitoring the General condition of the animals of the 2nd experimental group was regarded as satisfactory.
The histological pattern of the preparations of the pancreas in the 2nd experimental group on the 8th day since the introduction of alloxan differed significantly from the 1st experimental group, the control and placebo groups. Along with the pathological pattern of pancreatic tissue and inflammatory changes in it, in the preparations was monitored by a large number of islets of both small and medium and large sizes with enlightened cytoplasm, correct round shape, large, round nuclei containing nucleoli. Met Islands in its structure similar to the structure of islet apparatus of intact rats. After 1.5 months since the introduction of alloxan histological pattern in this group was characterized by signs of hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the pancreas. Observed a large number of Islands of different sizes, correctly rounded. The structure of islets and single β-cells was not altered, the nuclei in the cells are large, with rounded nuclei.
Primatological the study of the liver in the 2nd experimental group found organized beamed structure of the liver parenchyma in the greater part of the square of the drug. Around the larger vessels of moderate accumulation of dark-stained cells of lymphoid type. Sine waves are moderately dilated. The cytoplasm of most hepatocytes moderately oxytelinae, granular with small vacuoles. Compared to the 1st experimental group noted the appearance of normal hepatocytes. The nucleus of most cells clear, well-structured, well-colored with distinct nucleoli. Binucleate cells are rarely met.
CONCLUSION
Because of the selective cytotoxic effect of alloxan on cells of the pancreas in experimental animals in the control and placebo groups developed acute insulin deficiency, which, according to biochemical parameters were accompanied by severe hyperglycemia, hyperosmolarity, ketoacidosis, in combination with its own toxic effects of alloxan. Not correctable insulin insufficiency has led to the deaths of animals for 3-4 days since the introduction of alloxan. Despite pronounced degenerative changes in the pancreas of significant changes in the structure of the liver were found. Histological picture of the liver to a greater extent was characteristic of toxic damage to the liver cells (ketoacidosis, own toxic effect of alloxan), which presents degenerating hepatocytes without destroying the structure of the liver parenchyma. This suggests that due to acute is not correctable insulin deficiency in the application of toxic doses of alloxan animals of the control and placebo groups were killed before implemented compensatory-adaptive mechanisms associated with long chronic course of diabetes mellitus, which would be reflected in structural changes of the body concerned – the liver.
In contrast, in animals of the 1st experimental group that was exposed to the corrective influence of pEMP in the acute period and survived after administration of toxic doses of alloxan, remote morphological pattern in the pancreas, along with destructive changes were characterized by signs of regeneration of the damaged organ, and in the liver pronounced degenerative changes in the structure of the body. Such changes in the liver were caused by both the effects of acute cytotoxic effect of alloxan, and the impact of a number of pathological factors that appear in patients with chronic insulin deficiency and impaired carbohydrate metabolism. In the first phase correcting the effects of electromagnetic radiation converted by the tissues of the pancreas and spleen of newborn rat, the animals developed acute insulin deficiency (1st experimental group) stimulated activation of compensatory-adaptive mechanisms aimed at preserving life, as evidenced by the high survival of animals in the acute period (90%). In the second stage, given the presence of persistent pathological conditions in animals began to realize compensatory-adaptive mechanisms aimed at restoring lost function and normalization of carbohydrate homeostasis, which was accompanied by marked changes in the parenchymatous structure of the body concerned – the liver and activation of regeneration processes in the pancreas. About the successful implementation of compensatory-adaptive mechanisms spoke high survival of animals in this group throughout the observation period (75%), the positive dynamics of glucose in the blood and biochemical parameters in the serum (Fig. 2, 3, 4).
Unlike corrective effects of pEMP, preventive effects on animals of the 2nd experimental group had a cytoprotective effect on cells of the pancreas, probably by increasing tissue resistance to stress. Activation of compensatory-adaptive mechanisms in rats, the preventive effects of pEMP contributed 100% survival and the resistance of animals to the action of alloxan in the acute period, and later resulted in hypertrophic and hyperplastic changes in the pancreas, which were compensatory in nature, the preservation of the morphological structure of the liver.
CONCLUSIONS
1. A method of correction of experimental acute insulin deficiency in rats, based on the effects of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation of helium-neon laser, converted tissues of the pancreas and spleen of newborn rat.
2. In an experimental model of alloxan diabetes it is shown that the corrective effect of this type of radiation causes a decrease in the level of glucose in the blood to normal values at 65% of the animals and 75% survival rate.
3. When correcting the effect of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation, converted biostructures, on animals with experimental insulin deficiency implemented compensatory-adaptive mechanisms, leading to the normalization of biochemical parameters of blood serum and activation of regeneration processes in the tissue of the pancreas, but was accompanied by degenerative changes in the structure of liver tissue.
4. It is established that the preventive effect of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation that is converted by the tissues of the pancreas and spleen of newborn rat, prevents the increase of glucose level in the blood and provides 100% survival of animals during subsequent introduction of toxic doses of alloxan.
5. Based preventive effects of this radiation lies marked cytoprotective effect on cells of the pancreas that promotes normalization of biochemical parameters in the serum due to the development of hypertrophic and hyperplastic processes in the damaged body and the preservation of the structure of the liver tissue.
PRACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
The obtained results can be used for further investigation of pathophysiological mechanisms of action of low-intensity electromagnetic radiation on biological objects, as in acute insulin deficiency, and other pathological conditions of the body.
The list of scientific papers published on the topic of the thesis
1. The influence of modulated biostructures electro – magnetic radiation on the course of alloxan diabetes in rats / Garyaev PP, Kokaya A. A., I. Mukhina Century, Kokaya N. G. // Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, No. 2, 2007, S. 155-158.
2. The impact of the preventive effects of modulated bio – structures of electromagnetic radiation on morphological changes in the pancreas in rats with experimental insulin deficiency / Kokaya N. G., Kokaya A. A., I. Mukhina Century // proceedings of the final scientific conference “Tatyana’s day”. – Moscow – 2010.- S. 59.
3. Morphological changes in the pancreas of rats in the treatment of experimental insulin deficiency electromagnetic radiation / Kokaya N. G., Kokaya A. A., I. Mukhina Century // Proceedings of the report of the school for young researchers “basic science and clinical progress of medicine.” – Moscow – 2010.- S. 88.
4.The impact of corrective and preventive effects of modulated biostructures electromagnetic radiation on the course of experimental diabetes in rats / Kokaya N. G., Kokaya A. A., I. Mukhina Century // Proceedings of the 4th International scientific conference of young scientists. – Kursk – 2010.- C. 158-161.
5. Effects from exposure to electromagnetic radiation modulated tissue of the pancreas and spleen on the course of experimental diabetes in rats / Friedman M, Kokaya A. A., Kokaya N. G., I. Mukhina Century // Proceedings of conference “Psychotronic”- Kentucky, USA – 2010.-S. 22-25.
6. The influence of laser radiation on remote structural adjustment in the tissue of the pancreas in rats with acute insulin deficiency/ Kokaya A. A., Kokaya N. G., I. Mukhina Century. //
Abstracts of papers of the 2nd international conference “Fundamental and applied aspects of medical Primatology”.- Sochi-2011.- C. 293-301.
7. The impact of corrective and preventive effects of electromagnetic radiation, modulated biostructures, during acute insulin deficiency in rats / Kokaya N. G., Kokaya A. A., I. Mukhina Century Modern technologies in medicine, No. 3, 2011, S. 11-15.
8.Morphological changes in the pancreas of rats in the correction of acute insulin deficiency electromagnetic radiation, modulated biostructures / Kokaya N. G., Kokaya A. A.,I. Mukhina Century // the Natural and technical Sciences No. 3(53), 2011, S. 156-164.
9. The influence of modulated biostructures electromagnetic radiation on a remote adaptive structural adjustment of liver cells in rats with experimental diabetes mellitus / Kokaya N. G., Kokaya A. A., I. Mukhina Century // the Bulletin of new medical technologies No. 3, 2011, S. 123-126.
10. Remote adaptive structural rearrangement of the cells of the liver and pancreas of rats in the correction of acute insulin deficiency electromagnetic radiation, modulated biostructures / Kokaya A. A., Kokaya N. G., I. Mukhina Century / Medical almanac No. 5, 2011, S. 175-179.
The author expresses his sincere gratitude and deep appreciation to all the staff of the Central research Institute of the PFM Nigga and especially the staff of the Department of morphology and biochemistry, supervisor D. B. N., Professor I. Mukhina Century for high professionalism and wisdom teacher, K. M. N. Kokaya A. A., and L. Thelen, Director General of OOO “October shipbuilding-NN for sponsorship.